Excessive Sun Exposure and Aging
Basking in the warm glow of the sun can make us feel good, and in the short term, makes us look good. But excessive sun exposure at the beach or in tanning salons causes the majority of the sun damage that is associated with premature aging.
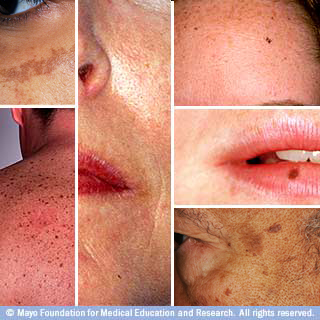
This sun damage accumulates over time and causes cosmetic defects such as uneven pigmentation (age spots, solar lentigines, melasma) and more serious problems like skin cancer.
The sun also causes the dilation of the facial blood vessels giving skin a mottled, reddish appearance, aging, collagen and elastin deterioration.
Aging of the skin is a process influenced by many different factors, including heredity, sun exposure, the environment, health habits, and general lifestyle. The sun and its ultraviolet (UV) rays have the greatest impact on how our skin ages.
Approximately 80 to 85 percent of our aging is caused by the rays of the sun.
As we age, the collagen and elastin fibers of the skin naturally weaken. This weakening happens at a much faster rate when the skin is frequently exposed to UV rays. The UV rays of the sun reach the skin in two different forms, as UVA and UVB rays.
Each of the rays influences the skin at a different level.
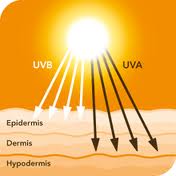 UVA rays, also
called the “aging rays”, contribute 90 to 95 percent of the
sun’s ultraviolet rays that reach the earth’s surface. These
rays weaken the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers, causing wrinkling
and sagging in the tissues.
UVA rays, also
called the “aging rays”, contribute 90 to 95 percent of the
sun’s ultraviolet rays that reach the earth’s surface. These
rays weaken the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers, causing wrinkling
and sagging in the tissues.
UVB rays, also referred to as the “burning rays”, cause tanning of the skin by affecting the melanomas, the cells of the epidermis that are responsible for producing melanin. Melanin is designed to help protect the skin from the sun’s UV rays, but can be altered or destroyed when large, frequent doses of UV light are allowed to penetrate the skin.
Although UVB penetration is not as deep as UVA, these rays are equally damaging to the sun and can damage the eyes as well. On a positive note, UVB rays contribute to the body’s synthesis of vitamin D and other important minerals.
Increasing The Sun’s Damaging Effects
Some people may be more at risk than others:
- Where you live: If you live close to equator, the sun is directly overheard and the UV rays are stronger.
- How do you live: sun damage accumulates over time-the more you are exposed, the more damaged your skin becomes. Apply sun protection every time you venture out.
- You medications: certain medications, such as antibiotics, burth control peels, cause heightened sensitivity to the sun.
- Genetics: if you are fair skinned with light hair (red or blond) and freckles, you are at high risk of developing sun damage and skin cancer.
- Cosmetic Procedures: microdermabrasion, chemical peel, laser resurfacing can intensify your sensitivity to the sun.
Sun Damage Prevention

- Protect yourself: Apply sun protection at least 30 SPF prior to every
time you are going to be in direct or indirect contact with the
sun.
Sun protectant ought to be applied to the face, ears, lips, neck, chest and arms. Do not forget to protect your scalp if you have bald spots or your hair is thinning. Put the protectant on 20 minutes before you will be in UV contact. For extended or intentional exposure when you are working, exercising, or relaxing outdoors, sun protectant should be reapplied every 2 to 3 hours. - Take cover: In order to minimize sun exposure, you should search for shade on every possible occasion. Firmly woven. loose-fitting, full-length clothing, and a wide-brimmed hat can offer additional protection. To help avoid damage to your eyes, sunglasses that block 99% to 100% of UV rays should be worn.
- Avoid the afternoon sun: UV rays are at its strongest between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Oppose the temptation: Refuse to give in to the desire to tan outdoors in natural light or indoors under artificial UV light (sun beds). UV rays enter the inner layers of the skin. I reply, the body produces additional melanin, that causes the skin to be obviously darker. A tan is proof that UV has damaged some of the skin’s cells that is not healthy or safe.
- Avoid exposing children younger than six months of age to the sun.
- Get expert advice: You should schedule regular appointments with your dermatologist for checkups of the skin, especially if any changes in coloration, size, or shape of mole are detected.

Treatment for Sun Damage and Aging
Treatment for sun damaged skin depends on which symptoms are present.
At Svetlana’s Skin Secrets we offer:
